Business electricity bills explained
Business electricity bills are very different from the simple home energy bills you might be used to.
They include lots of extra charges and taxes that can easily leave business owners feeling confused.
This guide provides a clear overview of how business electricity bills work, explaining the calculation of each individual charge and providing an annotated real-world example of a bill.
Here are the key parts of our guide:
- What is included in a business electricity bill?
- Business electricity bill breakdown
- The impact of tariff choice on business electricity bills
- Backdating of business electricity bills
What is included in a business electricity bill?
In this section, we explain the key charges included in business electricity bills, demonstrating how they are calculated and what they cover.
Electricity unit charges
Applies to: All types of business electricity bill.
All business electricity bills include a charge for each kWh of electricity used during the billing period, based on meter readings. The readings are either:
- Actual readings – Where you have submitted a meter reading to your supplier, or where a smart meter automatically provides the readings.
- Estimated readings – Where your supplier estimates your usage in the absence of actual meter readings.
Electricity unit charges on a business electricity bill are calculated as follows:
Unit charge in your business electricity tariff (p/kWh)
💡 Multi-rate business electricity meters have separate calculations for different times of the day, as defined in your tariff.
Business electricity unit costs pay for the following:
- Wholesale electricity purchases – Purchasing electricity from power generators such as UK wind farms, gas power plants, and nuclear power stations.
- Transmission Network Use of System charges (TNUoS) – Demand-based fees paid for using the national grid.
- Balancing Services Use of System charge (BSUoS) – Costs associated with keeping the electricity system balanced and ensuring supply meets demand in real time.
- Contracts for Difference levy – Energy suppliers pay a CfD levy for each MWh of power they supply to subsidise renewable energy developments.
- Renewable Obligation Certificates – Suppliers must purchase Renewable Obligation Certificates from eligible generators for each MWh of power supplied to business customers.
Electricity standing charge
Applies to: All types of business electricity bill, except zero standing charge tariffs.
A daily standing charge applies to most business electricity tariffs. It is calculated on business electricity bills as follows:
the number of days in the billing period
The daily standing charge pays for the following fixed costs:
- Distribution Use of System charges (DUoS) – Fixed charges associated with using your regional electricity grid.
- Meter maintenance and rental charges – Covers the costs incurred by your supplier to maintain traditional and smart energy meters.
- Meter operator charges – Additional fees paid by customers with half-hourly business electricity meters.
- Meter readings – The costs incurred by your supplier to arrange meter readings or pay for data transmission for automatic meter readings.
- Supplier margin – An additional margin to cover the operational costs of being an energy supplier, such as providing a customer service function.
Capacity charge
Applies to: Properties with half-hourly business electricity meters.
A capacity charge guarantees the availability of a certain Maximum Import Capacity (in kVA) of a business electricity connection for energy-intensive properties.
Capacity charges are typically applied as a fixed rate between 70p and 150p/kVA per month, calculated as follows:
Capacity unit rate (p/kVA)
Capacity charges are paid to the local distribution network operator. For more information, visit our guide to capacity charges.
Climate Change Levy
Applies to: All types of business except microbusinesses and charities.
The Climate Change Levy is a government tax charged for each kWh of electricity consumed on a business electricity bill.
From 1 April 2025 to 31 March 2026, the CCL rate is 0.775p/kWh. The total levy is calculated as follows:
The Climate Change Levy is designed to promote improvements in business energy efficiency.
VAT
Applies to: All types of business electricity bills.
VAT is a consumption tax that the UK government levies on the sale of goods and services.
VAT on business energy bills is charged at the following rates:
- Micro business electricity customers and charities – 5%
- All other non-domestic properties – 20%
The VAT charge on business electricity bills is calculated as follows:
Applicable VAT rate
Business electricity bill breakdown
The section below is a visual guide to the key components of a small business electricity bill. We’ve annotated specific sections of a real electricity bill to explain what they mean and how they work.
Summary of your charges and amount due
The first page of a business electricity bill typically provides the following summary:
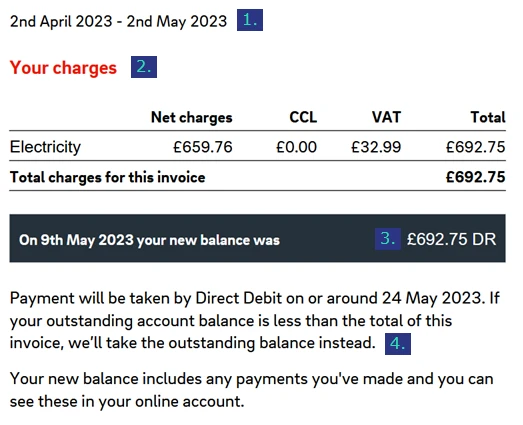
- Billing period – The date range over which the business electricity charges are calculated.
- Total electricity charges – The electricity costs incurred during the billing period. A detailed calculation is provided later in the bill.
- Balance due – The total amount due, calculated as the electricity charges plus any unpaid balances from previous months.
- Payment information – Instructions on how to pay the bill, or the date when payment will be automatically collected via direct debit.
Your tariff information
The next part of the bill displays information about your current business electricity tariff. Ofgem mandates that this information be shown for all small business energy customers.
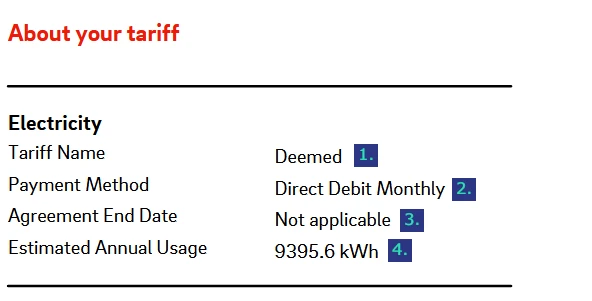
- Tariff name – The type of tariff being used, usually stated as “deemed”, “default”, “variable”, or “fixed”.
- Payment method – The agreed method of payment for your tariff.
- Agreement end date – The date on which fixed tariff rates will no longer apply.
- Estimated annual usage – The business electricity consumption that your supplier will use to estimate your bill if they have not received meter readings.
Your business electricity charges details
The final section of a business electricity bill provides a detailed calculation of your business electricity charges.
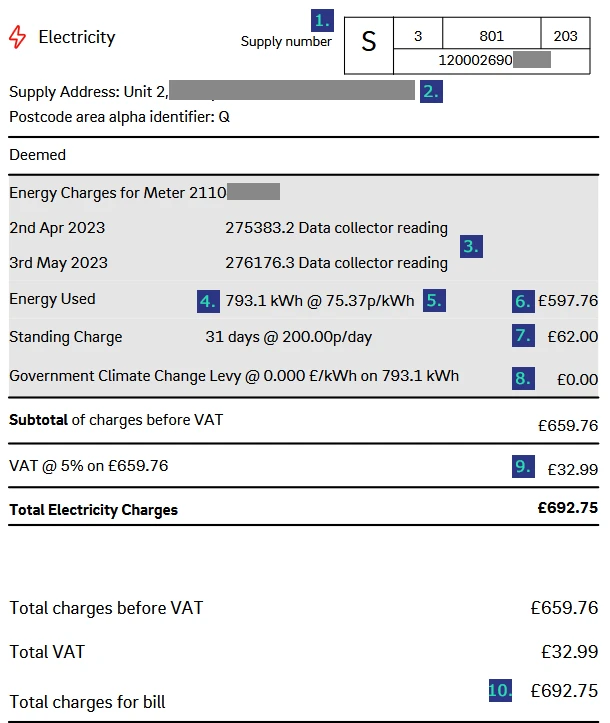
- The supply number – The supply number (MPAN) is a unique identifier associated with your electricity grid connection.
- Supply address – The address and meter number associated with your business electricity connection.
- Meter readings – The electricity meter readings at the start and end of the billing period.
- Electricity consumption – The electricity used during the billing period, calculated as the difference between the start and end meter readings.
- Unit rate – The business electricity prices per kWh in your electricity tariff.
- Unit charge – The electricity consumption figure multiplied by the unit rate.
- Standing charge – The daily standing charge in your tariff, multiplied by the number of days in the billing period.
- Climate Change Levy (CCL) – The Climate Change Levy rate multiplied by the electricity consumption in the billing period.
- VAT – VAT is added to all other charges on the bill at a rate of either 5% or 20%.
- Total electricity charges – The total charges incurred during the billing period.
💡 At Business Energy Deals, we are experts in helping companies compare business energy prices to secure the lowest possible charges on their business electricity bills.
The impact of tariff choice on business electricity bills
Business electricity bills generally follow the same format regardless of your tariff. However, the choice of tariff does have the following important impacts on your business electricity bills:
- Fixed tariff – The unit rate per kWh of business energy consumption is fixed on all bills during the term of the contract.
- Variable tariff – Your supplier may change the unit rate per kWh on future bills in line with market fluctuations.
- Pass-through tariff – In a pass-through business electricity bill, third-party distribution and transmission costs are charged separately from your unit rates and standing charges.
- Time of use tariff – The electricity unit charges section of your bill will show a separate calculation of consumption and unit rates for different times of day.
Use our business electricity comparison service to search the market for today’s best electricity tariffs.
Backdating of business electricity bills
Backdating is a billing process where a business energy supplier corrects the estimates used for meter readings on previous bills.
When you submit a meter reading, your supplier obtains a precise measurement of how much electricity your business has consumed. They will use this to recalculate previous consumption estimates on your latest business electricity bill.
Backdating can result in either an additional charge or a refund on your bill.
Unexpected charges from the backdating process are a frequent source of business energy supplier complaints.
We recommend regularly submitting meter readings or upgrading to a smart meter to avoid backdating issues on your business electricity bills.

