Distribution network operators
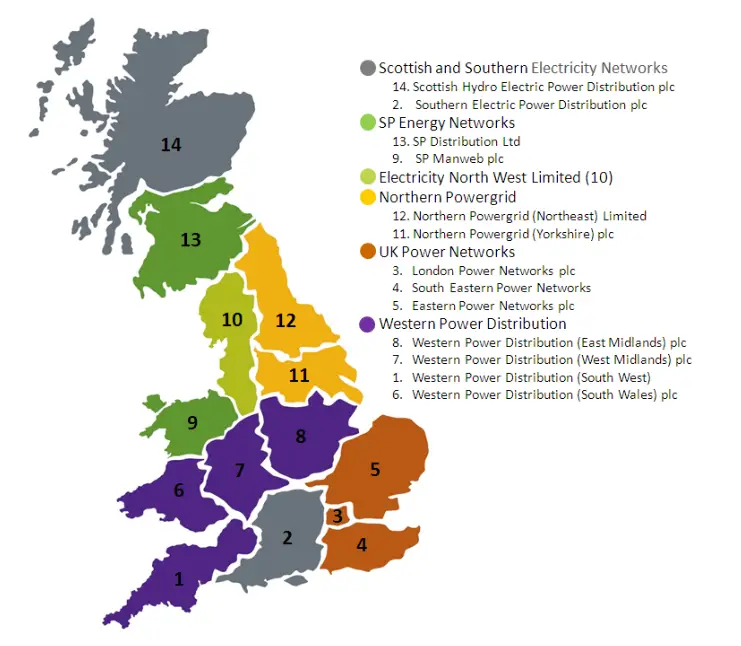
The British electricity grid is not a single continuous network. Instead, Britain is divided into 14 regional distribution grids, each managed separately by distribution network operators providing electricity to properties within their respective areas.
In this guide, we will explain the important role of distribution network operators in the British electricity grid.
What is a distribution network operator?
An electricity distribution network operator (DNO) manages the electricity infrastructure in a specific region, providing electricity connections to all homes and businesses.
To fully understand the role of a DNO, we will explain their infrastructure assets, responsibilities and how they earn money.
Distribution network operator infrastructure
A distribution network operator receives high-voltage electricity from the national grid. The DNO’s infrastructure reduces the voltage to 230V and distributes it to properties in the region.
This involves managing the following infrastructure:
- Overhead cables: Connecting to the national grid and distributing high voltage electricity to urban areas in the region.
- Substations: Facilities that step down the voltage using transformers to the 230 volts local properties use.
- Underground cables: Cables that distribute lower voltage electricity in an area, connecting individual properties.
Distribution network operator responsibilities
A distribution network operator is licensed by Ofgem with formal responsibility for:
- Network maintenance: Ensuring efficient and reliable operation of the local electricity distribution network.
- New connections: Providing new domestic or business electricity connections to any properties built in their region.
- MPAN: Managing Meter Point Administration Numbers (MPAN) allocated to electricity connections in their region.
- Renewables: Facilitating connections for small-scale renewables, such as wind farms and commercial solar panels, in their region.
Read our guide to how green business energy tariffs work to understand how green energy tariffs are delivered using regional distribution networks.
How do distribution network operators get paid?
Business electricity suppliers pay distribution network operators to distribute electricity to their individual customers.
Distribution fees are called Distribution Use of System (DUoS) charges and are carefully regulated by Ofgem.
Distribution fees do not normally appear separately on most business electricity bills but are included within unit business electricity rates.
💡 The distribution charges are different for each DNO. That’s why we ask for your postcode in our business energy comparison service.
How do I find my distribution network operator?
Here are the three easiest ways to identify the distribution network operator that manages your connection to the grid:
- Refer to the Distribution ID on your MPAN (indexed in the table below).
- Find your region in the table below and follow the link to your DNO.
- Use the Energy Network Associations ‘find my network operator‘ tool.
| MPAN Prefix | Region | Distribution Network Operator |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | East England | UK Power Networks |
| 11 | East Midlands | National Grid |
| 12 | London | UK Power Networks |
| 13 | North Wales, Merseyside and Cheshire | SP Energy Networks |
| 14 | West Midlands | National Grid |
| 15 | North East England | Northern Powergrid |
| 16 | North West England | Electricity North West |
| 17 | North Scotland | Scottish and Southern Energy |
| 18 | Central and Southern Scotland | SP Energy Networks |
| 19 | South East England | UK Power Networks |
| 20 | Southern England | Scottish and Southern Energy |
| 21 | South Wales | National Grid |
| 22 | South West England | National Grid |
| 23 | Yorkshire | Northern Powergrid |
Who are the electricity distribution network operators?
The 14 electricity distribution networks are owned by the following six companies:
- Scottish Power Energy Networks – Part of the Scottish Power group, which is also a business energy supplier, and owns a range of renewable electricity generation assets, including UK wind farms.
- National Grid (formally Western Power Distribution) – The National Grid DNO is a subsidiary of National Grid Plc, which also owns the high-voltage electricity network connecting the regional electricity distribution networks together.
- Northern Powergrid – Owned by Berkshire Hathaway, Northern Powergrid exclusively manages electricity distribution networks and is dedicated to delivering a reliable power supply while investing in network innovation.
- Electricity North West – Another privately owned electricity distribution company that focuses on providing a dependable power supply while investing in network resilience and environmental sustainability.
- Scottish and Southern Energy – A subsidiary of SSE plc, a business electricity and business gas supplier, and a major investor in UK renewables, including hydroelectric and wind power.
- UK Power Networks – UK Power Networks, owned by the Cheung Kong Group (CK Group), operates electricity distribution networks and focuses on ensuring reliable power delivery and infrastructure maintenance.
Distribution network operators by region
The distribution network operators in Britain are defined by their geographical areas. Each operator is responsible for distributing electricity to the homes and businesses within their region.
The following map shows the 14 different electricity distribution network regions:
What are Independent Distribution Network Operators?
An Independent Distribution Network Operator (IDNO) is a small sub-grid connected to a DNO.
Since 2004, Ofgem has allowed independent electricity distribution networks to connect between the existing DNOs and new property developments.
List of Independent Distribution Network Operators
The list of licensed independent distribution network operators is growing fast. Refer to Ofgem’s list of electricity licensees for the current list.
The Energy Network Association’s search tool can tell you if your electricity connection is managed by an Independent Distribution Network Operator.

