Commercial voltage optimisation
Voltage optimisation can be a quick and cost-effective way to reduce your business energy bills and carbon emissions by up to 12%, while also extending the lifespan of your electronic equipment.
But it’s not the right fit for every business. Voltage optimisation works best for sites that consistently receive more voltage than they need and use equipment that’s sensitive to voltage levels.
This guide helps businesses determine whether they can benefit from voltage optimisation. Here’s what we cover:
- How voltage optimisation for businesses works
- Commercial benefits of voltage optimisation
- Types of voltage optimisation units for businesses
- How to assess the suitability of voltage optimisation
- Voltage optimisation costs and savings
- Installing voltage optimisation in a commercial property
How voltage optimisation for businesses works
Voltage optimisation is a process that reduces the voltage from a mains supply to the optimum level required for the equipment that uses this power.
This section explains why the voltage supplied by the grid in Britain is often significantly higher than the optimum voltage level, and how a voltage optimisation unit solves this problem.
Optimum voltage level
Most electronic equipment sold in Britain is designed to operate most efficiently within the 220–230V range, which is the international standard.
Within this ideal range, motors, transformers, and lighting run cooler and more efficiently, using less power while also extending their working life.
Voltage from the national grid
In Britain, the supply voltage of the national grid is 230V (with a tolerance of +10% / -6%), meaning voltages can vary from 216V to 253V.
However, the average voltage supplied by the grid is 240V, which is significantly higher than the optimum voltage level. This is particularly problematic for commercial sites located close to electrical substations.
Voltage optimisation unit
A voltage optimisation unit adjusts the incoming voltage from a grid connection to match the optimum voltage required by the equipment used on site.
A VO unit is a metal-enclosed cabinet installed between the mains supply and the main distribution board. The diagram below shows the impact it has on a power supply.
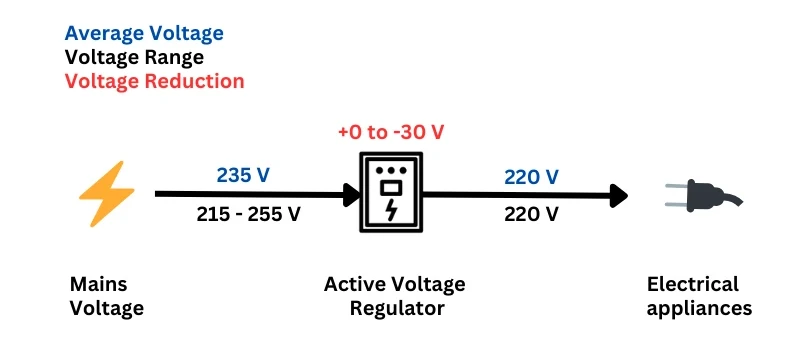
💡Voltage optimisation units can also perform the same role for energy-intensive commercial properties that use a 400V three-phase power supply.
Commercial benefits of voltage optimisation
This section summarises the three key benefits of a voltage optimisation system for large business energy customers.
Reduced energy consumption
Common electrical equipment such as lighting and heating will consume significantly less energy when supplied with electricity at the optimum voltage level.
Using a voltage optimisation unit can reduce the energy consumed at a commercial property, as recorded by a business electricity meter, by up to 12%.
Business electricity bills are calculated based on these meter readings, so a VO unit can significantly reduce energy costs.
Extended equipment lifespan
When voltage is consistently supplied above the optimum level, it accelerates wear and failure in motors, lighting, transformers, and air-conditioning systems.
Voltage optimisation helps equipment last longer, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Efficiency and sustainability goals
Installing a voltage optimisation system can support a business’s sustainability goals, particularly for businesses participating in the following schemes:
- Energy Savings Opportunity Scheme (ESOS) – Voltage optimisation can reduce the energy intensity ratio of commercial activities.
- Streamlined Energy & Carbon Reporting (SECR) – Voltage optimisation systems reduce kWh energy consumption and the associated carbon emissions for businesses.
Types of voltage optimisation units for businesses
This section explains the three main types of voltage optimisation equipment available to British businesses, and the situations where each is most effective.
Fixed voltage optimisation
Fixed voltage optimisation units reduce incoming voltage by a fixed percentage. They are typically configured to lower the average incoming voltage to 220V.
- Advantages: A simple, low-cost solution that is easy to install and maintain.
- Disadvantages: Does not respond to fluctuating voltages. May under-supply voltage if the incoming supply dips.
- Best for: Properties with a consistently high mains voltage and low sensitivity to voltage variation.
Dynamic voltage optimisation
A dynamic voltage optimisation unit monitors and adjusts the output voltage in real time to maintain a target voltage.
- Advantages: Always maintains voltage at the optimal level, delivering energy savings across a wide range of conditions.
- Disadvantages: Higher upfront costs and more complex to install and maintain.
- Best for: Properties with a variable supply voltage and voltage-sensitive equipment.
Solid-state voltage optimisation
This type uses advanced electronics to regulate voltage with high precision. In addition to voltage control, these systems can optimise a system’s reactive power demand.
- Advantages: Provides the most precise voltage control and can also reduce reactive power charges for a business.
- Disadvantages: The most expensive type of voltage optimisation unit, requiring more space and a temperature-controlled environment.
- Best for: Complex commercial properties with a three-phase power supply.
How to assess the suitability of voltage optimisation
Voltage optimisation is usually only beneficial for your business if your site consistently receives mains voltage above 230V and you use energy-intensive equipment sensitive to voltage fluctuations.
This section explains how to assess whether these conditions apply to your business.
Assess electrical equipment for voltage optimisation
Whether voltage optimisation is suitable for your business depends on the types of electrical equipment you use.
Some equipment is highly sensitive to voltage and can see noticeable energy savings, while other equipment already regulates voltage internally, so optimisation makes little or no difference.
Here is a table showing the energy-saving potential of using voltage optimisation for different types of equipment:
| Device Type | Examples | Load Type | Energy Savings Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incandescent Lighting | Halogen lamps, traditional filament bulbs | Resistive | High |
| Electric Heaters | Space heaters, panel heaters | Resistive | High |
| Induction Motors | HVAC fans, pumps, lifts, compressors | Inductive | Medium to High |
| Refrigeration Equipment | Commercial fridges, freezers, cold rooms | Inductive | Medium |
| Fluorescent Lighting | T8/T12 tubes with magnetic ballasts | Inductive | Medium |
| LED Lighting | Modern LED panels or bulbs | Electronic | Low |
| Computers & Servers | Office PCs, network equipment, data centres | Electronic | Low |
| Audio-Visual Equipment | Televisions, projectors, sound systems | Electronic | Low |
For more information on assessing the relative energy use of electrical equipment, visit our guide to business energy consumption.
Overall power demand
Investing in voltage optimisation equipment is typically not worthwhile for small business energy customers where power demand is low, as the potential for savings is likely to be minimal.
Instead, we recommend considering voltage optimisation solutions for properties with maximum demand exceeding 100 kVA.
💡Properties with a maximum demand of 100 kVA or more are fitted with half-hourly electricity meters.
Power quality assessment
Before investing in voltage optimisation equipment, assessing the voltage levels supplied to your property is essential.
Some properties may already receive a stable 220V supply, making voltage optimisation unnecessary.
The voltage of an electrical supply to an individual property depends on the local infrastructure of your distribution network operator and the power demand from other nearby properties.
A professional power quality assessment involves connecting a voltage data logger to your mains supply to continuously measure voltage variability over a representative period of one or two weeks.
If the recorded voltage is consistently:
- Above 235–240V: Voltage optimisation is likely to deliver significant savings
- Within 220–235V: Voltage optimisation might offer only limited benefits.
Voltage optimisation costs and savings
A voltage optimisation system requires a significant upfront capital investment, which should pay for itself through long-term reductions in energy consumption.
This section explains the typical installation and maintenance costs and quantifies the expected long-term savings from installing a VO unit.
Voltage optimisation purchase and installation costs
Installing a voltage optimisation system involves a significant upfront investment for both the hardware and installation.
The cost of a system typically depends on the capacity of a specific business electricity connection and the type of system used. Here are indicative prices for single VO unit installations:
| System Type | Typical Cost Range (Installed) |
|---|---|
| Fixed VO Unit | £3,000 – £10,000 |
| Dynamic VO Unit | £7,000 – £25,000 |
| Solid-State VO Unit | £20,000 – £50,000+ |
The prices above include hardware and installation, based on indicative supplier pricing from UK VO manufacturers and commercial installation case studies.
Ongoing costs of voltage optimisation
Voltage optimisation systems require minimal maintenance and should continue to operate for between 15 and 25 years before replacement is needed.
Most businesses enter into a support contract, typically costing a few hundred pounds per year, with their VO provider to carry out basic annual checks.
Voltage optimisation energy cost savings
Installing a voltage optimisation system can save British businesses between 7% and 12% on the unit rate of their business electricity prices.
Some voltage optimisation providers claim the system can pay for itself through reduced costs from a business energy supplier in as little as two years.
💡At Business Energy Deals, we specialise in helping companies reduce their energy costs. Use our business electricity comparison service today to find out how much you can save.
Installing voltage optimisation in a commercial property
This section summarises working with a voltage optimisation provider to install a VO unit at a commercial property. We recommend choosing a provider with experience installing VO systems for businesses of a similar size or within the same sector.
Site survey
A voltage optimisation provider will typically conduct an on-site survey to recommend the appropriate VO type and capacity and estimate the potential energy savings and return on investment for your specific property.
A site survey will typically:
- Review the distribution board layout
- Identify main loads and circuits
- Consider any sensitive equipment that may need bypassing
- Determine whether a fixed or dynamic system is most suitable
- Determine the system’s capacity requirements
The provider will issue a technical proposal and cost quotation following the site survey.
Installation and commissioning
A voltage optimisation provider will arrange for a certified engineer to carry out the installation of the equipment.
VO equipment is typically installed between the mains incoming supply and the distribution board.
To minimise disruption from the temporary power outage required, installation is often scheduled for evenings or weekends.
Integration with EMS
A voltage optimisation system can be integrated with an Energy Management System (EMS) to provide live voltage readings and log voltage fluctuations and fault events.
An EMS can help verify that the VO system is delivering the expected improvements in business energy efficiency.
Expected installation timescale
The complete voltage optimisation installation process typically takes between 4 and 8 weeks.
Here’s what to expect at each stage:
- Initial assessment and site survey: 1-2 weeks
- System design and planning: 1-2 weeks
- Equipment procurement and preparation: 1-3 weeks
- Installation and commissioning: 1 day on site

